E. Gleeson1, M. F. Shaikh1, A. E. Poor1, P. A. Shewokis1, J. R. Clarke1, D. S. Lind1, W. C. Meyers1, W. B. Bowne1 1Drexel University College Of Medicine,Surgery,Philadelphia, Pa, USA
Introduction: Pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) is a high-risk procedure. There is need for simple validated risk models to better identify 30-day mortality. The goal of this study was to identify independent, preoperative risk factors and to develop a simple risk score to predict 30-day mortality after PD.
Methods: We reviewed all patients who underwent PD from 2005-2012 in the ACS-NSQIP databases. Logistic regression was used to identify preoperative risks for 30-day mortality from a development cohort ([DEVEL] random 80% of the database). The WHipple-ABACUS score was created using weighted beta coefficients and predictive accuracy was assessed on the validation cohort ([VALID] the remaining 20%) using a receiver operator characteristic curve and calculating the area under the curve (AUC).
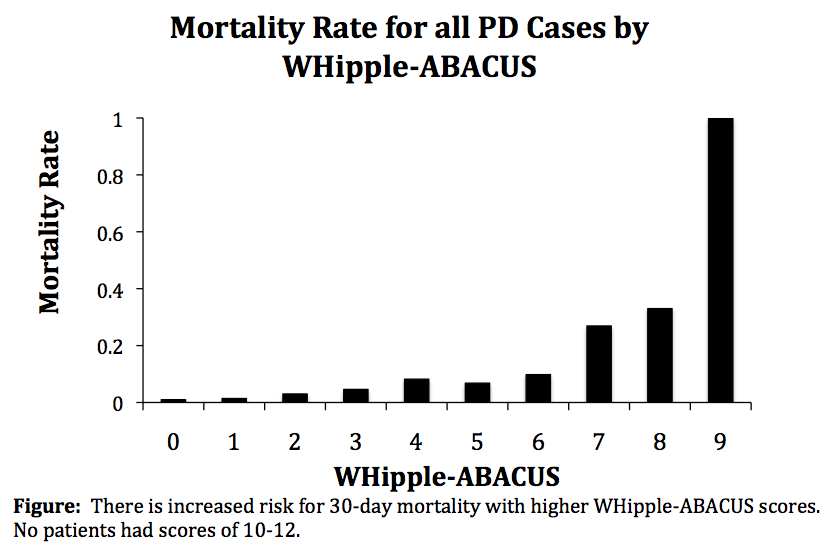
Results: The 30-day mortality rate was 2.7% for patients who underwent PD (n=14,993). The DEVEL identified 8 independent risk factors: hypertension with medication, history of cardiac surgery, age > 62, bleeding disorder, albumin <3.5g/dL, disseminated cancer, use of steroids and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). The score created from weighted beta coefficients (see Figure) had an AUC=0.71 (95%CI 0.66 to 0.77) using the VALID. Using the WHipple-ABACUS score: WHipple-ABACUS = hypertension With medication + History of cardiac surgery + Age>62 + 2*Bleeding disorder + Albumin<3.5g/dL + 2*disseminated Cancer + 2*Use of steroids + 2*SIRS, mortality rates increase with increasing score (p<0.001).
Conclusion: While other risk scores exist for 30-day mortality after PD, we present a simple, validated score developed using exclusively preoperative predictors that surgeons should use to optimize co-morbidities and inform patients of risk with this procedure.