Y. Kim1, F. Gani1, A. Ejaz2, L. Xu1, J. K. Canner1, E. B. Schneider1, T. M. Pawlik1 1Johns Hopkins University School Of Medicine,Baltimore, MD, USA 2University Of Illinois At Chicago,Chicago, IL, USA
Introduction: Most studies report data on readmission within 30-days of discharge from the same hospital following a single procedure. Readmission after combined multiple surgical procedures is common, but data comparing patterns of readmission are rare. We therefore sought to define the incidence of early versus late hospital readmission among patients experiencing combined major surgeries.
Methods: Patients discharged after ten major surgical procedures (CABG, AAA, carotid endarterectomy, aortic valve replacement, esophagectomy, gastrectomy, pancreatectomy, pulmonary resection, hepatectomy, colorectal resection) between 2010 and 2012 were identified from a large employer-provided health plan. Unplanned readmissions among patients who underwent combined surgical procedures were analyzed.
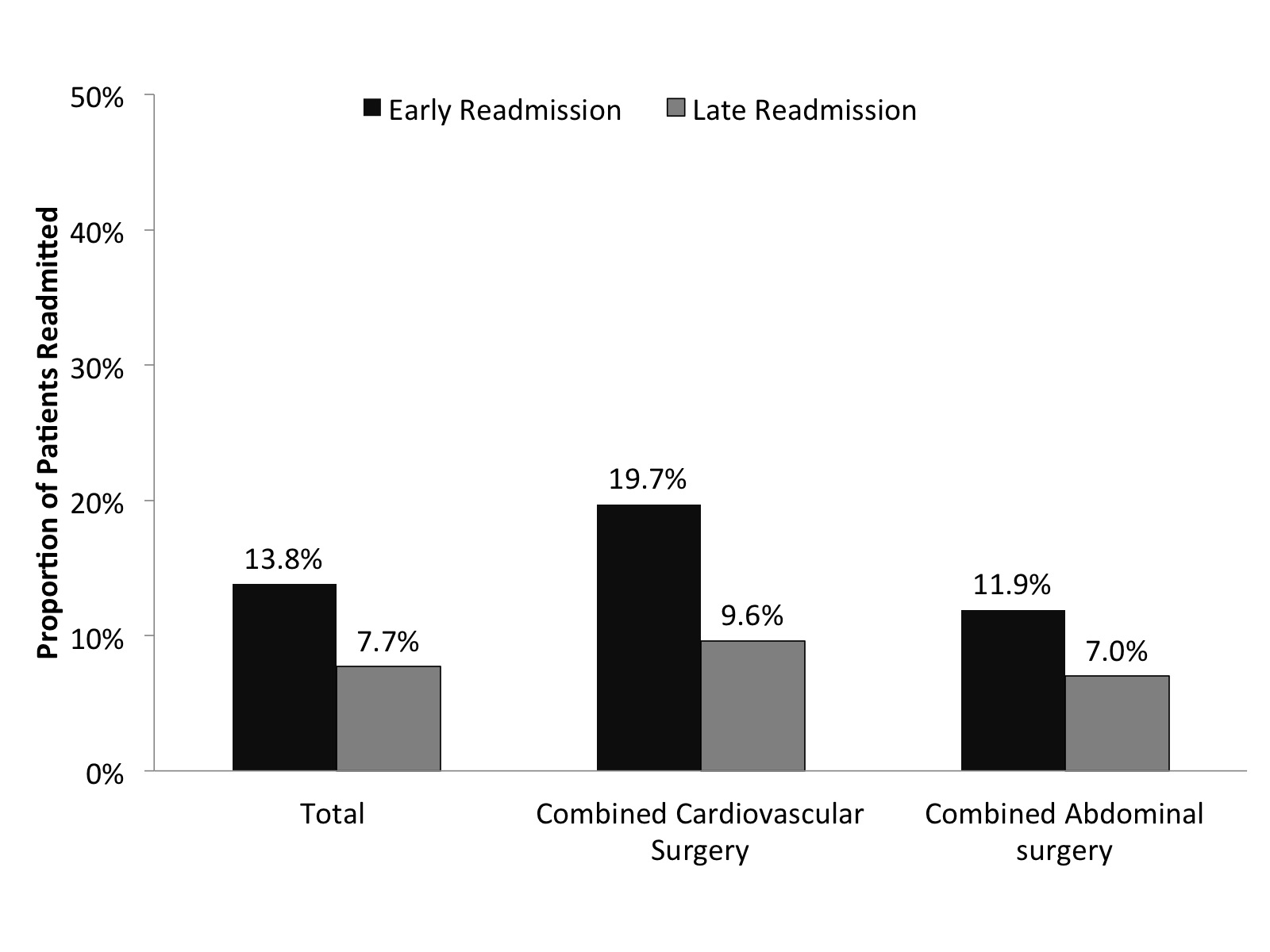
Results: 3,358 patients experiencing combined major surgeries were identified? median patient age was 59 years, 69.6% were male, and 53.6% had Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) of ≥2. Median length-of-stay (LOS) was 8 (IQR 6-13) days. 2,933 (84.4%) of patients were discharged home of which 41.0% (n=1,162) were discharged home under care. 3.8% (n=127) of patients had died during the index hospitalization. Among the 723 (21.5%) patients who experienced readmission, 465 (13.8%) had a readmission within 30-days while 258 (7.7%) were readmitted within 31-90 days (Figure). Median time to readmission was 19 (IQR 8-44) days. In-hospital mortality (1.7% vs. 1.5%) and length-of-stay(4 vs. 3 days) were comparable among patients readmitted early and late(both P>0.05). On multivariable analyses, CCI (≥2: Odds Ratio [OR] 1.63, 95%CI 1.37-1.94), LOS (OR 1.02, 95%CI 1.01-1.03) and postoperative complication (OR 1.26, 95%CI 1.06-1.51) were associated with 90 day readmission. The most common reason for early and late readmission were postoperative infection (12.7%) and pneumonia (3.9%), respectively.
Conclusion: More than one third of readmissions occurred beyond 30-days after combined major surgical procedures. Assessment of only 30-day same hospital readmissions underestimates the actual impact of readmission among patients undergoing complex procedures.