M. E. Mitchell1, D. Beste1 1Children’s Hospital Of Wisconsin,Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery/Surgery/Medical College Of Wisconsin,Milwaukee, WI, USA
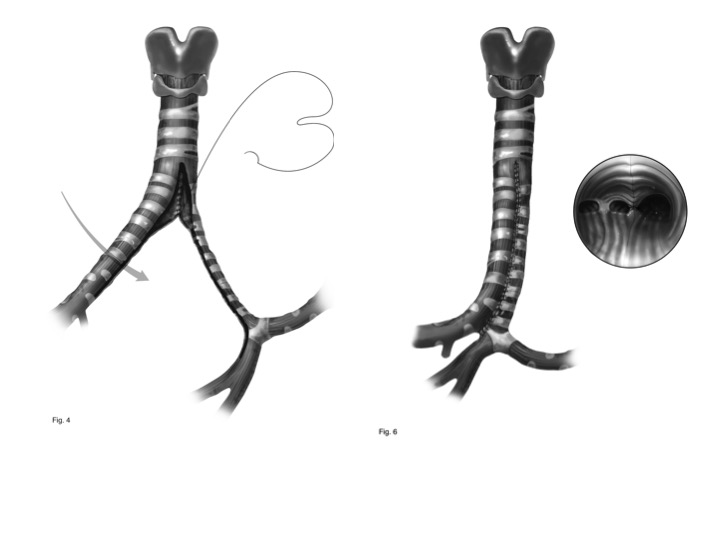
Introduction: Slide tracheoplasty has been used widely for reconstruction of long segment tracheal stenosis secondary to complete tracheal rings. We present the successful use of a variation of slide tracheoplasty, side to side Bronchus Suis Tracheoplasty in three extreme cases of complete tracheal rings, tracheo-bronchial hypoplasia and tracheal bronchus in premature neonates and infants.
Methods:
Three patients age less then 60 days presented with long segment tracheal stenosis in the context of a Bronchus Suis, complete tracheal rings, and a pulmonary artery sling. All patients had inability to ventilate consistently despite intubation and required urgent tracheal reconstruction. All patients underwent long segment tracheoplasty consisting of a side to side anastamosis between the Bronchus Suis and the hypoplastic trachea and right lower lobe bronchus.
Results:
There was no mortality. One patient who underwent initial slide tracheoplasty and required tracheostomy, was ultimately decannulated following side to side tracheal reconstruction. The other two patients who underwent one stage side to side tracheoplasty as neonates did well and were discharged without ventilatory support.
Conclusion:
Side to side tracheal reconstruction using a Bronchus Suis to augment a severely hypoplastic trachea is feasible in severe cases of long segment tracheal stenosis.