W. He1, Z. Chang1, B. Liu1, X. Cheng1, T. Bambakidis1, I. Halaweish1, Y. Li1, P. Patrick2, V. Nikolian2, H. B. Alam1 1University Of Michigan,General Surgery,Ann Arbor, MI, USA 2University Of Michigan Health System,Ann Arbor, MI, USA
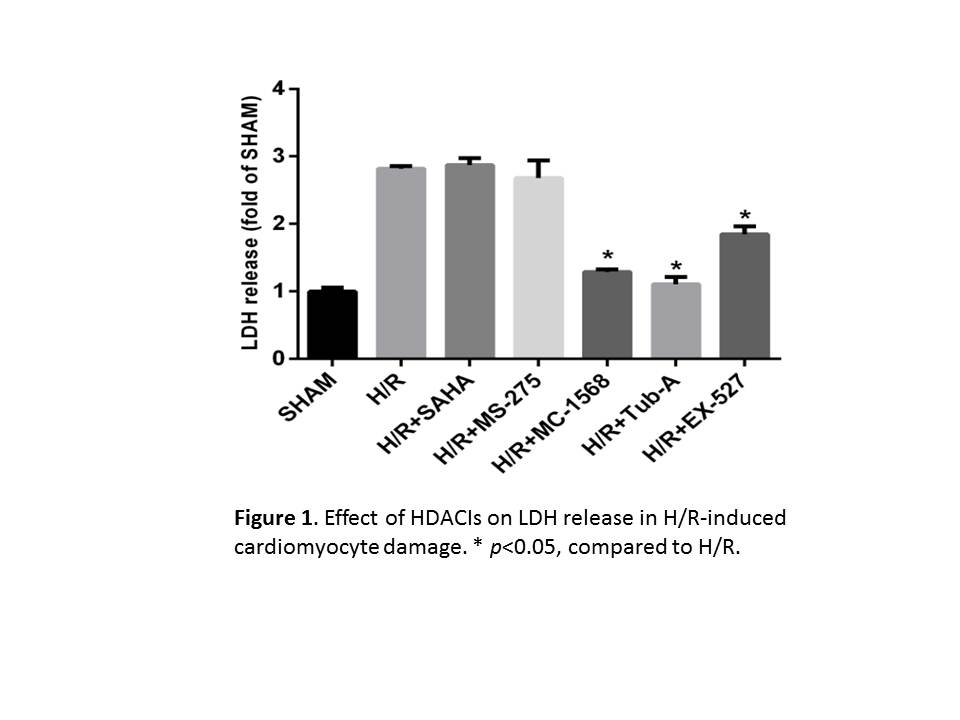
Introduction: We have previously shown that histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) preserve organ function and improve survival in a rat model of hemorrhagic shock. It remains unknown whether the different types of HDACIs differ in their cytoprotective potential. Here we used an in vitro model of hypoxia/ reoxygenation (H/R) to assess whether different HDACIs, such as SAHA (pan), MS-275 (class I), MC-1568 (class IIa), Tubastatin-A (Tub-A, class IIb), and EX-527 (class III), could protect the cardiomyocytes from injury. The most effective agent was also subjected to a mechanistic study.
Methods: Experiment I: H9c2 cardiomyocytes from ATCC were subjected to an in vitro model of H/R (12/8 hours), and treated with or without SAHA, MS-275, MC-1568, Tub-A, or EX-527. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an indicator of cellular toxicity, in cell culture media was detected by a LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit. The levels of acetylated histone H3 and acetylated α-tubulin were measured by Western blots. Experiment II: Tub-A was chosen for further investigation to analyze the underlying protective mechanisms. Cultured H9c2 cells were randomly divided into Sham control, H/R, and H/R+Tub-A groups. Expression of phospho-Akt (p-Akt)/Akt, phospho-mTOR (p-mTOR)/mTOR, phospho-p70s6k (p-p70s6k), phospho-rpS6 (p-rpS6)/rpS6 proteins were determined by Western blots. In addition, the changes in expression of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3)-II, a marker of autophagy, were assessed.
Results: High levels of acetylated histone H3 were detected in all of the HDACI treated-groups, while acetylated α-tubulin were only seen in Tub-A or SAHA treated-groups. Moreover, MC-1568, Tub-A, or EX-527, but not SAHA, or MS-527, markedly improved cell viability and decreased LDH release (Fig 1, p<0.05). Pro-survival effect of Tub-A was further confirmed by TUNEL assay. In addition, Tub-A treatment stimulated expression of p-Akt, p-mTOR and p-p70S6 kinases, as well as p-rpS6, in H9c2 cells. Expression of LC3-II was also significantly decreased in the Tub-A group.
Conclusion: HDACIs improve cell viability in a model of cardiomyocyte hypoxia/reoxygenation, with class IIa, IIb, and III inhibitors showing superior efficacy. This effect, at least in part, is due to the activation of AKT- mTOR- rpS6 signaling pathway.